Polychloroprene
Polychloroprene (CR)
Neoprene is a commercial name for polymers comprised of chloroprene. Polychloroprene’s overall physical characteristics classify it as a general-purpose elastomer. Excellent aging characteristics in ozone and weather environments, along with abrasion and flex cracking resistance, justify the general-purpose categorization.
Polychloroprene is alkali and acid resistant, flame retardant, and suitable for petroleum based oils. Animal and vegetable fats and greases also provide a highly stable environment for this polymer. Polychloroprene is noted for good compression set resistance, excellent flex fatigue resistance, and resistance to weather and ozone. Its excellent adhesion to metals makes polychloroprene ideal for molding with metal inserts.
Polychloroprene is not effective in aromatic and oxygenated solvent environments.
Compound 482BJ
- High tensile and tear strength
- Excellent flex fatigue resistance
- Excellent serviceability in repeated distortion applications (o-ring drive belts)
- Good for refrigerants
Compound 337Z, 323AR, 405A, 405DY
- General purpose neoprene compounds in a range of hardnesses
- Good weather, ozone, and flex fatigue resistance
- Moderate resistance to petroleum oils and chemicals
Compound 486CT
- Excellent aging characteristics
- Proven in a variety of gasket and washer applications
| Compound | Hardness Shore A | Tensile MPa | Tensile psi | Elongation (%) | Oil Aging Volume Swell (Change %) 70hr at 100°C/212°F ASTM #1 | Oil Aging Volume Swell (Change %) 70hr at 100°C/212°F IRM 903 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 486CT | 70 | 13.0 | 1880 | 200 | -2 | +41 |
| 482BJ | 70 | 18.3 | 2650 | 350 | +5 | +63 |
| 337Z | 50 | 10.3 | 1500 | 500 | -5 | +60 |
| 323AR | 60 | 11.0 | 1600 | 450 | +1 | +58 |
| 405A | 80 | 13.8 | 2000 | 220 | -2 | +48 |
| 405DY | 90 | 12.4 | 1800 | 100 | -1 | +35 |
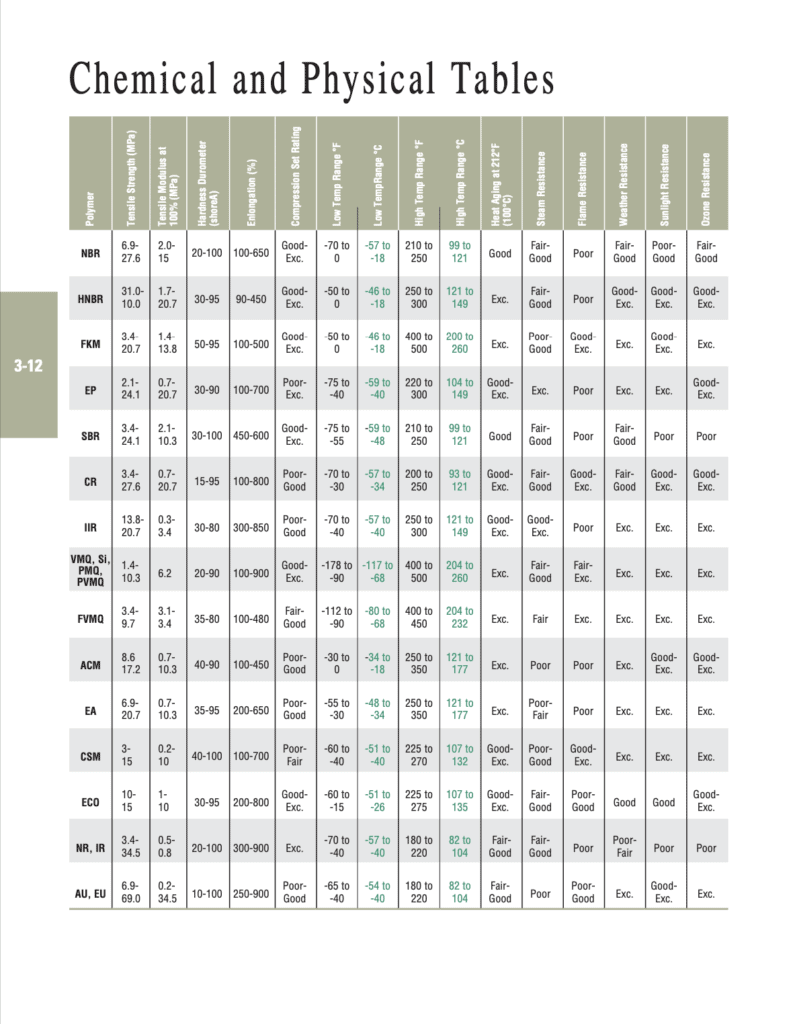
Chemical and Physical Tables
Click below to view the Elastomers/Materials: Chemical and Physical Tables PDF